Your credit score is a three-digit number that can make or break your financial opportunities in the United States. Whether you’re applying for a mortgage, seeking a car loan, or hoping to snag a premium credit card, your credit score acts like a financial report card, telling lenders how trustworthy you are with borrowed money. Understanding what is a good credit score in USA is crucial for navigating loans, securing better interest rates, and even renting an apartment or landing a job. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down credit score ranges in the USA, compare FICO vs VantageScore, explore lender requirements for loans, and share actionable tips on how to improve your credit score. By the end, you’ll know exactly where you stand and how to boost your score to unlock better financial prospects.
Why Your Credit Score Matters
A credit score reflects your creditworthiness, summarizing your history of borrowing and repaying money. Lenders, landlords, and even some employers use it to gauge your financial reliability. A higher score can mean lower interest rates, better loan terms, and easier approvals, while a lower score might lead to rejections or costly terms. As of 2025, the average FICO score in the USA is 715, and the average VantageScore is 702, both falling within the “good” range. But what exactly qualifies as a good credit score, and how can you achieve or surpass it? Let’s dive in.
Understanding Credit Score Ranges in the USA
Credit scores in the USA typically range from 300 to 850, with higher scores indicating better creditworthiness. Both major scoring models—FICO and VantageScore—use this range, though their categories and thresholds differ slightly. Below is a detailed breakdown of credit score ranges in the USA for both models.
FICO Credit Score Ranges
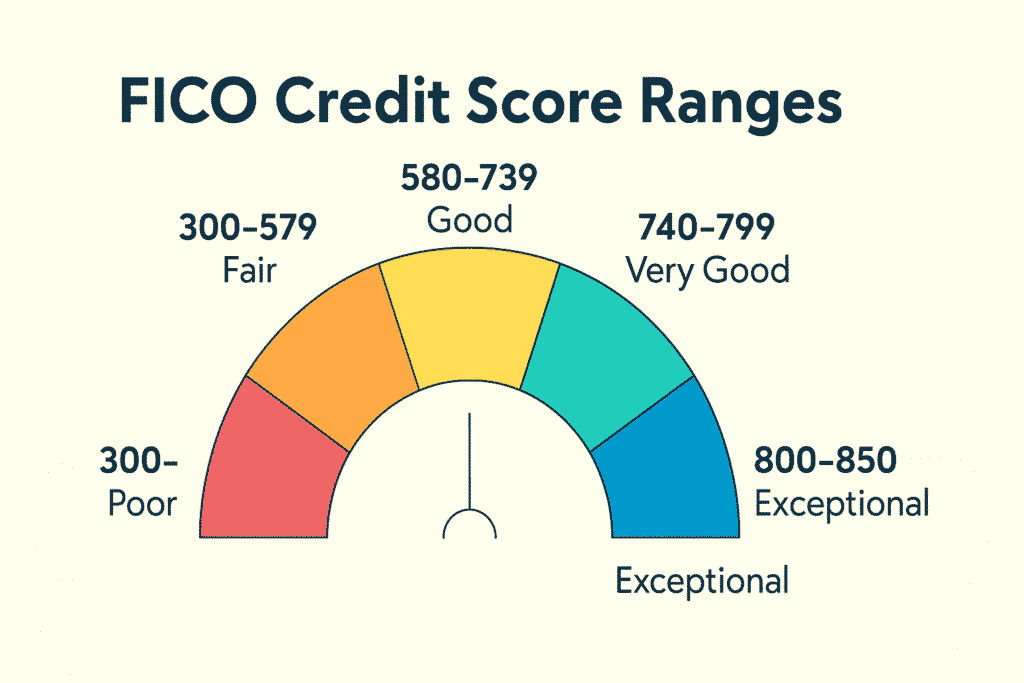
FICO, developed by the Fair Isaac Corporation, is the most widely used credit scoring model, employed by 90% of top lenders. Here’s how FICO categorizes scores:
- Exceptional (800–850): Borrowers in this range are considered low-risk, often securing the best interest rates and loan terms. About 21.2% of Americans have an exceptional FICO score.
- Very Good (740–799): These borrowers still enjoy favorable terms, though not always the absolute best. A score of 760 or higher often unlocks the best mortgage rates.
- Good (670–739): This is the sweet spot for most Americans, with 71.2% having a score of 670 or higher in 2024. You’ll qualify for most loans and credit cards but may not get the lowest rates.
- Fair (580–669): Considered subprime, borrowers in this range face higher interest rates and stricter terms. About 16.6% of Americans fall here.
- Poor (300–579): These scores indicate significant credit risk, making approvals for loans or credit cards challenging. Roughly 12.1% of Americans have poor scores.
VantageScore Credit Score Ranges
VantageScore, created by Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion, is gaining traction but is less common than FICO. Its ranges are:
- Super prime (781–850): Equivalent to FICO’s exceptional range, offering the best terms.
- Prime (661–780): Considered good to very good, this range provides access to most credit products at competitive rates.
- Near Prime (601–660): Borrowers may face higher rates and limited options.
- Subprime (300–600): High-risk borrowers often struggle to secure credit.
What is a good credit score in USA? For FICO, a score of 670–739 is considered good, while VantageScore defines 661–780 as good to very good. These ranges qualify you for most financial products, though higher scores (740+) yield better terms.

FICO vs VantageScore: What’s the Difference?
When exploring what is a good credit score in USA, it’s essential to understand the two primary scoring models: FICO vs VantageScore. While both aim to predict your likelihood of repaying debt, they differ in methodology, weighting, and usage.
FICO Score
- History: Introduced in 1989, FICO is the industry standard, used in 90% of lending decisions.
- Versions: Multiple versions exist, like FICO Score 8 (most common for general lending), FICO Score 2, 4, and 5 (used for mortgages), and industry-specific scores like FICO Auto Score (250–900 range).
- Factors: FICO scores are calculated based on:
- Payment history (35%)
- Amounts owed/credit utilization (30%)
- Length of credit history (15%)
- New credit (10%)
- Credit mix (10%)
- Usage: Preferred by mortgage lenders (especially for Fannie Mae/Freddie Mac loans), credit card issuers, and auto lenders.
VantageScore
- History: Launched in 2006 by the three major credit bureaus to compete with FICO.
- Versions: VantageScore 3.0 and 4.0 use the 300–850 range. Older versions (1.0 and 2.0) ranged from 501–990.
- Factors: VantageScore weights factors differently:
- Payment history (40%)
- Credit utilization and debt (20%)
- Credit age and mix (20%)
- New credit (10%)
- Available credit (3%)
- Usage: Used by some credit card issuers (e.g., Synchrony Bank) and free credit monitoring services like CreditWise and Credit Karma.
Key Differences
- Data Sensitivity: VantageScore can generate a score with just one month of credit history, while FICO requires six months.
- Late Payments: VantageScore penalizes late mortgage payments more heavily than FICO.
- Collection Accounts: VantageScore ignores paid collection accounts, while FICO ignores only those under $100 or paid medical collections.
- Additional Data: VantageScore includes rent and utility payments when reported, unlike FICO.
Which is more accurate? Neither is inherently more accurate; the choice depends on the lender. For mortgages, focus on your FICO score, as it’s required by government-backed entities like Fannie Mae. For credit cards or personal loans, either score may be used.
What is a Good Credit Score in USA for Loans?
When determining what is a good credit score in USA for specific financial products, lender requirements vary. Below, we outline typical credit score thresholds for common loans as of July 2025.
Credit Score for Mortgage Approval
- Conventional Mortgages: A minimum FICO score of 620 is typically required, though 740+ secures the best rates.
- FHA Loans: No strict minimum, but many lenders require at least 580–620.
- VA Loans: No official minimum, but lenders often prefer 620+.
- New Standards (Q4 2025): Starting late 2025, mortgage lenders may use FICO Score 10 T and VantageScore 4.0 for loans sold to Fannie Mae/Freddie Mac, potentially shifting requirements.
Example: Sarah, with a 720 FICO score, qualified for a conventional mortgage but paid slightly higher interest than her friend with a 760 score, saving thousands over the loan’s life.
Credit Score for Car Loan
- Prime Rates: A credit score for car loan approval of 661+ (VantageScore) or 670+ (FICO) qualifies for competitive rates, with 720+ unlocking the best terms.
- Subprime Borrowers: Scores below 600 may lead to high interest rates or smaller loan amounts.
- FICO Auto Score: Many auto lenders use industry-specific FICO Auto Scores (250–900), where 670–739 is good.
Example: John’s 680 FICO score got him a car loan, but his 8% interest rate was higher than the 4% offered to borrowers with 760+ scores.
Credit Cards and Personal Loans
- Rewards Credit Cards: Typically require a FICO score of 670–739 or higher.
- Personal Loans: A score of 670+ (FICO) or 661+ (VantageScore) ensures better rates, though subprime borrowers may qualify with higher interest.
- SBA Loans: For small business loans, a minimum score of 140–160 is needed for prescreening, but most lenders prefer 670+.
A good credit score in USA (670–739 for FICO, 661–780 for VantageScore) generally ensures approval for most loans and credit cards, but aiming for 740+ maximizes savings.
How Are Credit Scores Calculated?
Understanding how credit scores are calculated can help you take control of your financial future. Both FICO and VantageScore rely on data from your credit reports (maintained by Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion), but they weigh factors differently.
FICO Score Factors
- Payment History (35%): Paying bills on time is the biggest factor. Even one late payment can drop your score significantly, and delinquencies stay on your report for seven years.
- Amounts Owed/Credit Utilization (30%): This measures how much of your available credit you’re using. Keep your credit utilization ratio below 30% (e.g., $300 used out of a $1,000 limit).
- Length of Credit History (15%): Longer credit histories boost scores. This includes the age of your oldest account, newest account, and average account age.
- New Credit (10%): Multiple hard inquiries (from applying for new credit) can lower your score. Rate shopping for mortgages or auto loans within 14–45 days counts as one inquiry.
- Credit Mix (10%): Managing various credit types (e.g., credit cards, mortgages, auto loans) shows responsibility.
VantageScore Factors
- Payment History (40%): Similar to FICO, on-time payments are critical.
- Credit Utilization and Debt (20%): Lower utilization and debt levels improve scores.
- Credit Age and Mix (20%): A longer history and diverse credit types help.
- New Credit (10%): Fewer inquiries are better.
- Available Credit (3%): Having more available credit can boost your score.
Fun Fact: VantageScore includes rent and utility payments when reported, which can help those with thin credit files. FICO typically doesn’t.
How to Improve Your Credit Score
Improving your credit score takes time, but consistent habits can yield significant results. Here are actionable tips to improve your credit score:
- Pay Bills on Time: Set up automatic payments to avoid late payments, which can hurt your score for up to seven years.
- Reduce Credit Utilization: Keep your credit card balances below 30% of your limit. Pay down high balances or request a credit limit increase (without increasing spending).
- Avoid New Hard Inquiries: Space out credit applications by at least six months. When shopping for mortgages or car loans, complete inquiries within a 14–45-day window.
- Keep Old Accounts Open: Closing old credit cards can shorten your credit history and reduce available credit, lowering your score.
- Diversify Credit Types: If possible, maintain a mix of revolving (credit cards) and installment (auto loans, mortgages) accounts.
- Check Your Credit Report: Errors or fraudulent activity can drag down your score. Dispute inaccuracies with Experian, Equifax, or TransUnion via AnnualCreditReport.com.
- Use Experian Boost: This free service adds on-time utility, phone, and streaming payments to your Experian credit report, potentially raising your FICO score by 13 points on average.
- Consider a Secured Credit Card: If you have poor or no credit, a secured card (requiring a deposit) can help build your score with responsible use.
- Pay Off Collections: VantageScore ignores paid collection accounts, and FICO ignores small or medical collections once paid.
Example: Lisa had a 620 FICO score due to high credit card balances. By paying down her cards to 20% utilization and setting up auto-payments, her score rose to 680 in six months, qualifying her for a better car loan rate.
Free Tools to Check Your Credit Score
Monitoring your credit score for Good Credit Score in USA is easier than ever with free tools and apps. Checking your own score doesn’t hurt it (it’s a soft inquiry). Here are some reliable options:
- AnnualCreditReport.com: Get free credit reports from Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion weekly. You can pay extra for your VantageScore.
- myFICO: Offers free access to your FICO Score 8 from Experian and highlights factors affecting your score.
- CreditWise (Capital One): Provides free VantageScores from TransUnion, plus dark web monitoring. Open to non-cardholders.
- Chase Credit Journey: Free VantageScore from TransUnion, available to everyone.
- Credit Karma/Credit Sesame: Offer free VantageScores and personalized tips to improve your score.
- Bank and Credit Card Apps: Many issuers like American Express, Capital One, and Synchrony provide free FICO or VantageScores to cardholders.
Tip: Check your score monthly to track progress and spot issues early. Use multiple tools to monitor both FICO and VantageScore, as they may differ.
Additional Tips for Building Credit
- Become an Authorized User: If a trusted friend or family member adds you to their credit card, their positive payment history can boost your score.
- Credit-Builder Loans: These small loans, offered by some credit unions, report payments to bureaus, helping build credit.
- Limit Credit Applications: Applying for multiple cards or loans in a short period signals risk to lenders.
- Monitor for Fraud: Sign up for alerts from credit bureaus or services like Experian to catch unauthorized activity early.
The Impact of a Good Credit Score in USA
Having a good credit score in USA opens doors to financial opportunities:
- Lower Interest Rates: Save thousands on mortgages, car loans, and credit cards.
- Easier Approvals: Qualify for loans, apartments, and even some jobs.
- Higher Credit Limits: Increase your available credit, improving utilization ratios.
- Better Insurance Rates: Many insurers use credit-based insurance scores to set premiums.
For example, a 760 FICO score might secure a 3.5% mortgage rate, while a 660 score could result in a 4.5% rate, costing an extra $50,000 over a 30-year loan.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Credit Today
Understanding what is a good credit score in USA is the first step toward financial empowerment. A score of 670–739 (FICO) or 661–780 (VantageScore) is considered good, qualifying you for most loans and credit cards, though 740+ unlocks the best terms. By focusing on timely payments, low credit utilization, and responsible credit habits, you can steadily improve your score. Use free tools like myFICO, CreditWise, or Credit Karma to monitor your progress and catch errors early. Improving your credit is a marathon, not a sprint, but the rewards—lower rates, better terms, and more opportunities—are worth the effort.
For more such information about Good Credit Score in USA and blogs stay tuned with usamainland.com